Overview
This custom programming language is a small, interpreted language built from scratch using Python. (took me 50+ hours)
The language uses core compiler/interpreter concepts including lexical analysis, parsing, and interpretation.
Language Processing Pipeline
Language Syntax
Basic Syntax Rules
| Element | Syntax | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Comments | # This is a comment |
Single line comments using the # symbol |
| Integer Declaration | age = int(15) |
Declare and initialize an integer variable |
| String Declaration | name = string("Jim") |
Declare and initialize a string variable |
| Output Statement | say("Hello World") |
Print text or variable values to output |
| Variable Output | say(variableName) |
Print the value of a variable |
| Repeat Block | repeat 3 { |
Repeat the statements inside the braces a specified number of times |
| Arithmetic Operators | +, -, *, / |
Supports arithmetic in expressions and assignments |
| If Statement | if x > 5 { |
Conditionally execute statements if the condition is true |
| Function Definition | function name { |
Define a reusable block of code with a name |
| Function Call | call(name) |
Execute a previously defined function |
Code Examples
Hello World Program
say("Hello, World!")
Variable Declaration and Usage
age = int(16)
name = string("Alice")
# Output variables
say(name)
say(age)
Repeat Block Demo
repeat 4 {
say("hello!")
}
Arithmetic Operators Demo
minutes_in_a_day = int(60 * 24)
say(minutes_in_a_day)
# More complex expression
result = int((2 + 3) * 4 - 6 / 2)
say(result)
If Statement Demo
minutes = int(60 * 24)
if minutes > 100 {
say("there are more than 100 minutes in a day!")
}
# If with equality
x = int(5)
if x == 5 {
say("x is five!")
}
Function Demo
function hello {
say("Hello, World!")
}
# Call the function
call(hello)
# Function with multiple statements
function greet {
name = string("Alice")
say(name)
say("Welcome to our language!")
}
call(greet)
Technical Architecture
Lexer (Tokenizer)
Reads the code and splits it into pieces called tokens, like words and symbols.
Parser
Uses these tokens to build a tree that shows the program's structure.
Interpreter
Walks through the tree and runs the program step-by-step.
Symbol Table
Keeps track of variables, functions, their types, and current values while the program runs.
Token Types
The lexer recognizes the following token types:
- Keywords: int, string, function, call
- Identifiers: Variable names, function names
- Literals: String literals, integer literals
- Operators: Assignment (=), arithmetic operators (+, -, *, /), comparison operators (==, !=, >, <, >=, <=)
- Delimiters: Parentheses, braces, quotes
- Functions: say
- Comments: Lines starting with #
Getting Started
Requirements
This project requires NO pip imports!
To run programs in this custom language, you need:
- Python 3.6 or higher installed on your system
- The github repository cloned
- A text editor to write your programs
Running Your First Program
Follow these steps to create and run your first program:
# 2. Write your program:
say("Hello from my custom language!")
# 3. Run using the python file:
# python run.py hello.txt
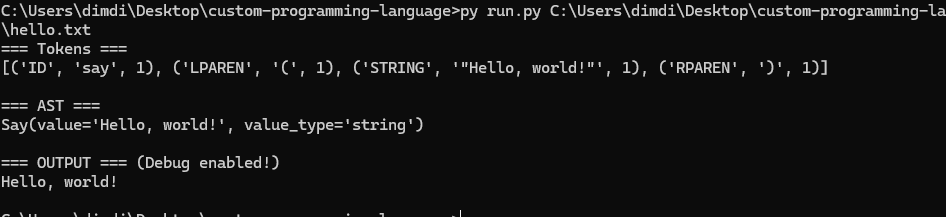
Debug Mode
Enable debug mode to see how your program is processed: